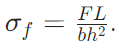Bending testing is a core mechanical test that evaluates a material’s flexural strength, ductility, and resistance to fracture under static bending loads. It’s widely used for brittle or semi-brittle materials (e.g., metals, plastics, ceramics) and structural components.
Bending Test Principle:
Bending testing applies a three-point or four-point bending load to a standardized specimen, causing it to deform (elastic then plastic) until fracture or a specified deflection. The key principle is stress distribution across the specimen cross-section:
The outer surface of the bent specimen is in tension, the inner surface in compression, and the neutral axis (center) has no stress.
The test measures the maximum bending stress (flexural strength) the material can withstand before failure, or its deflection at a given load (reflecting ductility).
How the Bending Test Works?
Step 1: Specimen PreparationFabricate specimens to standard dimensions (e.g., rectangular bars for metals/plastics, prisms for concrete). Common sizes: 10mm×10mm×100mm (metals) or 40mm×40mm×160mm (cement mortar).Ensure the specimen surface is smooth, free of cracks or defects, and the cross-section is uniform.
Step 2: Test SetupChoose between two common loading methods:
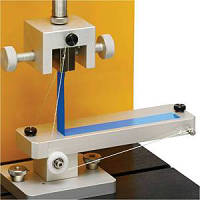
Three-point bending: Place the specimen on two supports (span L), apply a single load at the midpoint. Simple setup, widely used for general materials.
Four-point bending: Place the specimen on two supports, apply two symmetric loads (equidistant from each end). Creates uniform bending stress in the middle section, ideal for brittle materials (avoids stress concentration).
Step 3: Loading & Data Collection
Apply load at a constant rate (specified by standards, e.g., 2mm/min for metals, 0.5mm/min for plastics) using a universal testing machine.Record the load-deflection curve in real time—tracks how the specimen deforms under increasing load.
Step 4: Calculation of Key Indicators
Flexural strength (σf): Maximum bending stress before fracture, calculated as:
Three-point bending: 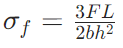 (where F = maximum load, L = span, b = specimen width, h = specimen height).
(where F = maximum load, L = span, b = specimen width, h = specimen height).
Four-point bending: 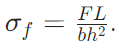
Flexural modulus (Ef): Stiffness of the material, derived from the linear elastic segment of the load-deflection curve.Deflection at fracture: Indicates ductility—larger deflection means better resistance to brittle fracture.














































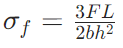 (where F = maximum load, L = span, b = specimen width, h = specimen height).
(where F = maximum load, L = span, b = specimen width, h = specimen height).